Implementing color masks in Godot
Masks are a powerful feature of different graphics editors. Can we implement them in Godot engine similarly?
🔗What is a color mask and why do you need it?
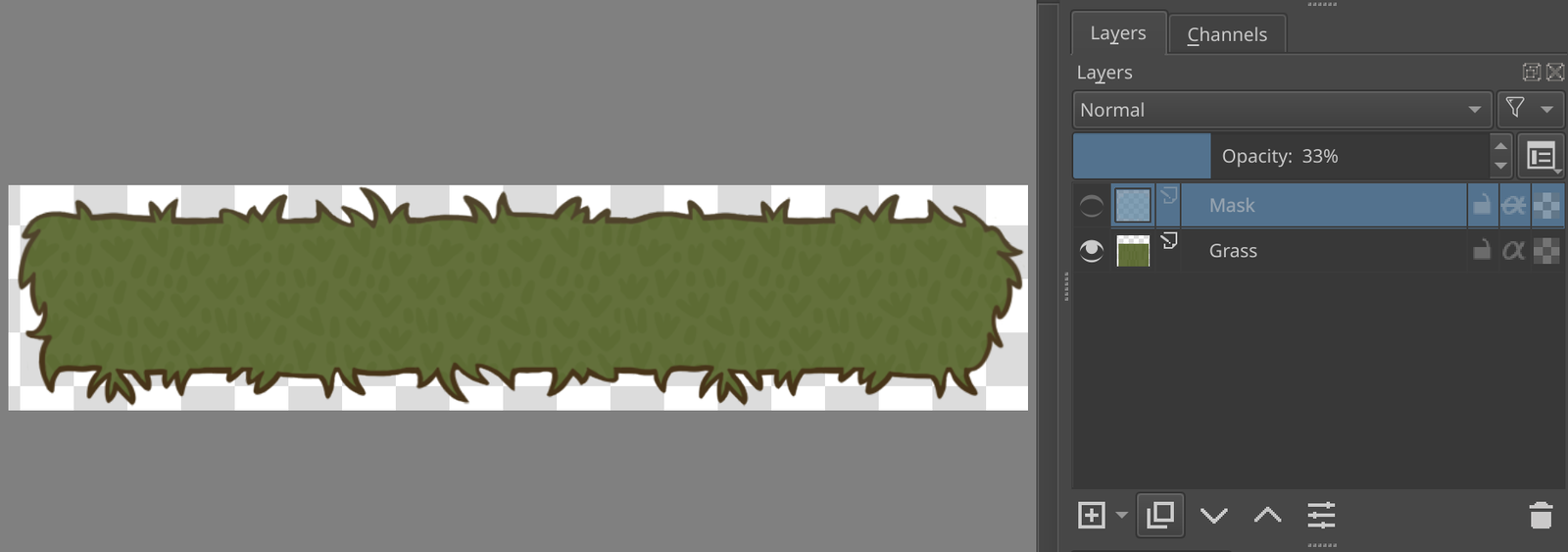
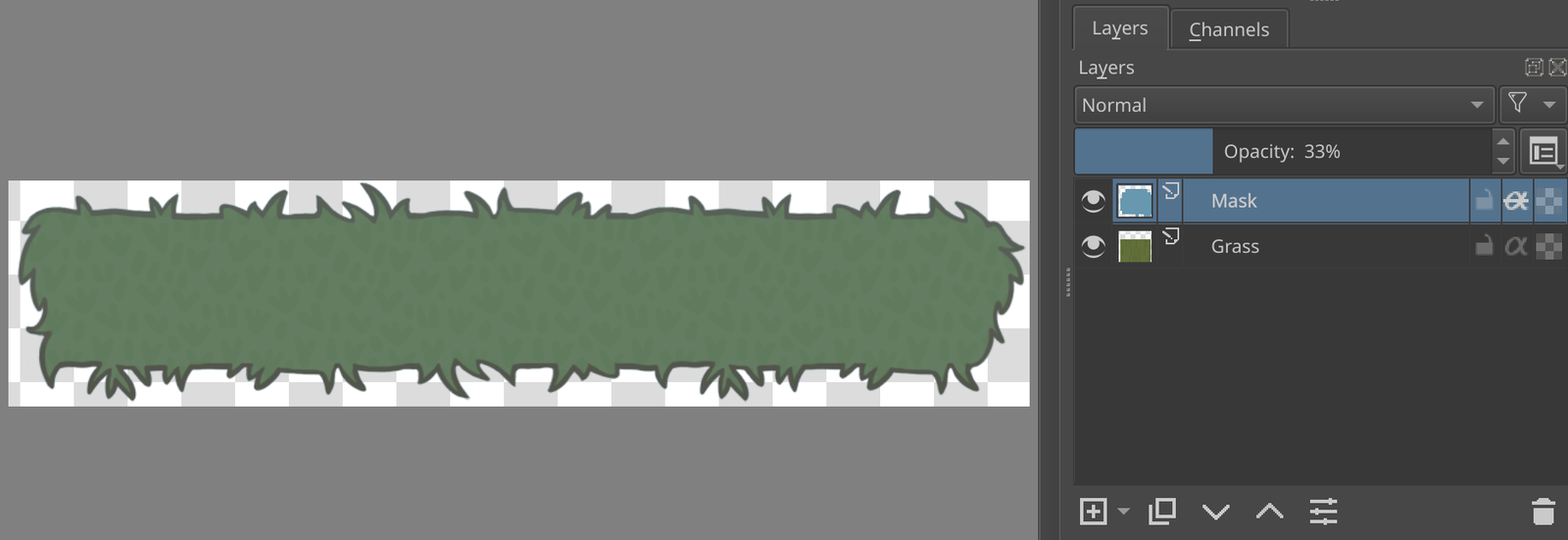
In many graphics editors (e.g. Krita, Photoshop) there is a thing named color mask. This is a convenient way to change the color of your image or parts of it, trim the image into a specific shape, etc. Consider these images with the mask off and then on:
As you can see, the mask is defined by two parameters:
- Color (in this case it’s
#6798b0) - Opacity of the mask layer (
33%)
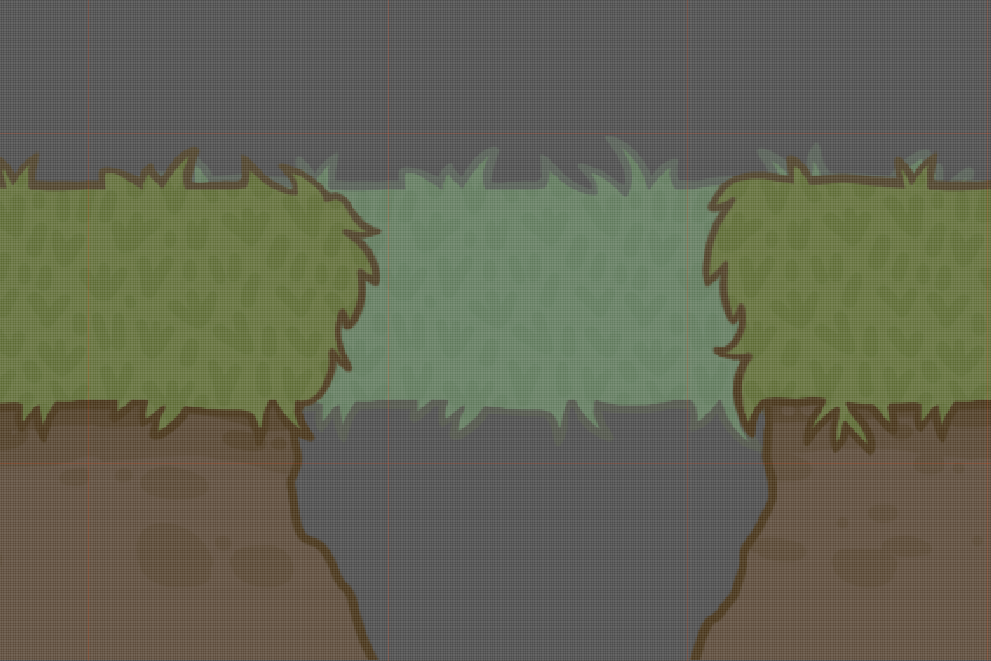

Result
Today, we will try to use color masks in Godot to implement the effect of aerial perspective. This is a very useful effect as it enables you to save some resources since you don’t need to have separate sprites for “close” and “far” layers. Take a look at the image above: this effect makes grass on the background look like it is further away and the Player will treat it like “inactive” and won’t try to walk on it.
🔗Creating and storing a mask
Godot already has a modulate property in every CanvasItem instance, but there is a problem with alpha-channel: if we set it, then the whole layer becomes transparent instead of just setting the “mix ratio”. To fix this we will write a shader!
Hot tip Shader is a tiny program that is executed by GPU.
There are two major modes in which shaders operate: Vertex and Canvas.
Vertex shader can alter an object’s form, while Canvas shader works on pixel-level.
Again, we want to “mix” the colors of the original image with the colors of the mask. Image Colors are stored in Texture that we will iterate through pixel-by-pixel during shader execution. But where should we keep the “mask”?
Luckily, shaders have inputs, so we can feed it with the needed info. The most effective storage for a “mask” that I found is a Gradient: Gradient selector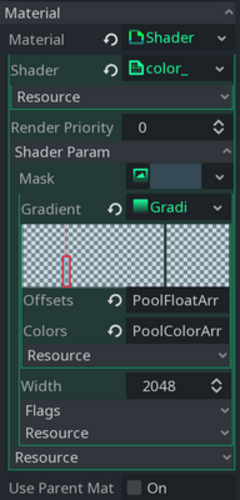
Yep, we are creating a gradient with only one component (aka step, vertical line in the center), so it is not a gradient :)
Hot tip To remove a gradient step, just right-click on it, to add a new step use left-click
We can choose the step’s color using this selector: Color selector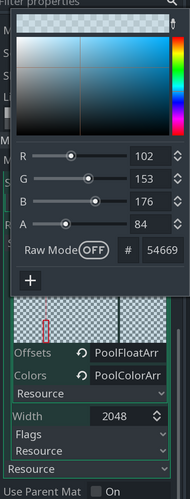
As you can see, it has all the needed parameters: RGB and alpha-channel.
Here is the shader itself, with comments:
shader_type canvas_item;
// Disable unneeded features
render_mode blend_disabled, unshaded;
// We'll take out the mask as input. In the editor it'll look like a gradient selector
uniform sampler2D mask: hint_white;
// This function is used to manipulate every pixel of the texture - right what we want
void

